As the New Year begins, let us also start a new!

NATURE
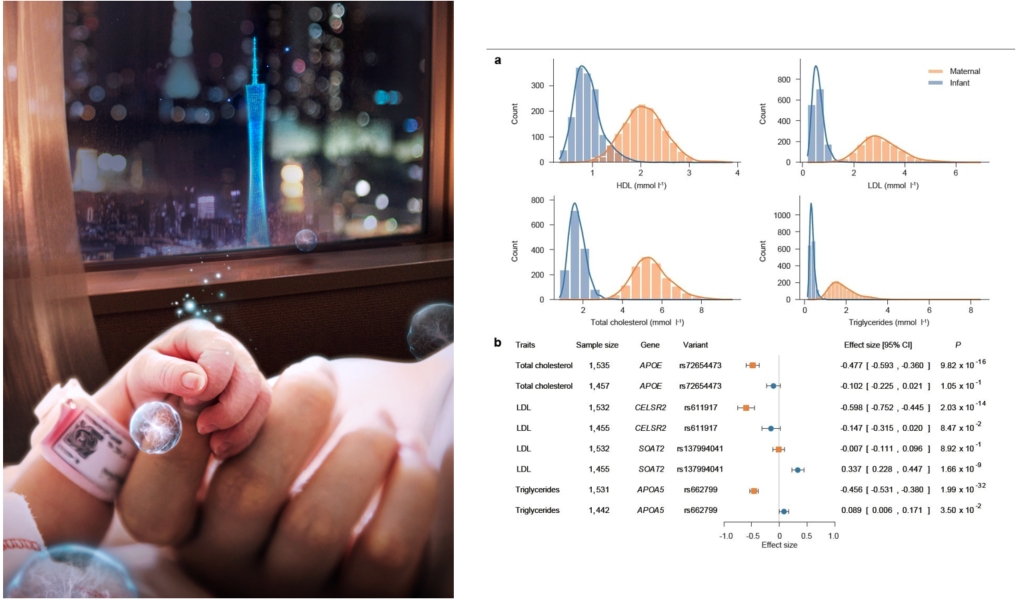
Fetal growth and development are affected by the maternal intrauterine environment and the fetus's own genetics, but it is not clear what role the intrauterine environment and genetic effects play in the growth and development of the fetus. In January 2024, BIGCS published a paper entitled "The Born in Guangzhou Cohort Study Enables Generational Genetic Discoveries" in the international journal Nature, revealing the impact of genetic factors and intrauterine environment on the health of offspring.Shaping Our Future: Envisioning 2050
The birth cohort study will promote the development of research in child health-related fields, facilitate the early prevention of major diseases, and reduce the social burden of diseases. Over 3,000,000 high-quality biological samples with epidemiological information will realize the rapid translation of scientific research results, shorten the distance between "lab and clinic" and increase the value of clinical applications, thus promoting the development of translational medicine and contributing to the socio-economic prosperity of South China. We firmly believe that today's 20 minutes will open up a brand new 20 years for us.
Our Team
Born in Guangzhou Cohort Study is one of the most innovative and dynamic sections in our center, with Epidemiology, Data Management, Cohort Operation, Bioinformatics and Biobanking teams. All team members graduated from famous universities at home and abroad, including maternal and child health, epidemiology, health statistics, obstetrics and gynecology, pediatrics, nutrition, pediatric health, molecular biology, bioinformatics, psychology and so on. Cumulatively, the team has trained one provincial and ministerial-level discipline leader, three doctoral directors, six master's directors, 17 high-level talents, eight postdoctoral fellows, 13 PhDs and 19 master's degree holders, of which three PhDs and eight master's degree holders have been jointly trained with famous overseas universities. The whole team adheres to the spirit of "there is no perfect individual, only a perfect team", pools wisdom, sails through thick and thin, and makes progress hand in hand.